What is Hard Water?

Shop Our Products

Freedom RV Water Softener System
Specifically for RV and fifth-wheel owners, this high-quality system guarantees your RV’s water is pure,



Have you ever turned on your tap, noticed a strange taste, or seen white deposits on your dishes? You might be dealing with hard water. But what exactly is hard water, and why does soft water matter?
Already have a water softener but think it may be time to upgrade? Read out guide on 6 things that mean you need a new water softener.
The Science Behind Hard Water
Hard water is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium. These minerals are picked up as water moves through soil and rock, dissolving small amounts of naturally occurring minerals and carrying them along. The more calcium and magnesium the water absorbs, the harder it becomes.
Mineral Breakdown
- Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3): The most common cause of water hardness, calcium carbonate can cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. This compound is abundant in limestone and chalk, making it a prevalent source of hardness in water supplies.
- Magnesium: Often found alongside calcium, magnesium also contributes to hardness and can lead to similar scaling problems. Magnesium-rich minerals such as dolomite and magnesite dissolve into groundwater, increasing the hardness.
- Other Minerals: While calcium and magnesium are the primary culprits, other minerals like iron can also be present in hard water, adding to its effects. Iron can cause reddish-brown stains and impact the taste and odor of water.
Grading Water Hardness
Water hardness is typically measured in grains per gallon (GPG) or parts per million (PPM). Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Soft Water: 0-3.5 GPG or 0-60 PPM
- Moderately Hard Water: 3.5-7 GPG or 60-120 PPM
- Hard Water: 7-10.5 GPG or 120-180 PPM
- Very Hard Water: Over 10.5 GPG or 180 PPM
Understanding the hardness of your water can help you decide on the best course of action for treatment and maintenance. Water hardness can be measured using test kits available for home use or by sending a sample to a laboratory for more precise results.
Issues Caused by Hard Water
Hard water might seem harmless, but it can cause a range of problems, both for your home and your health.
- Scale Buildup: Over time, the minerals in hard water can accumulate and form scale deposits inside pipes, water heaters, and appliances. This buildup can reduce efficiency, leading to higher energy costs and potential equipment failure. For example, a scaled-up water heater must work harder to heat water, using more energy and raising your utility bills.
- Soap Inefficiency: Hard water makes it harder for soap to lather and rinse away, leading to soap scum in sinks, bathtubs, and on your skin. This inefficiency means you need to use more soap or detergent to achieve the same level of cleanliness, increasing your household expenses.
- Skin and Hair Issues: The minerals in hard water can dry out skin and hair, leading to irritation and potential damage. Hard water can strip away natural oils, leaving skin feeling dry and itchy and hair looking dull and lifeless. Over time, this can exacerbate conditions like eczema or dermatitis.
- Stained Fixtures: The calcium and magnesium in hard water can leave unsightly stains on fixtures, dishes, and laundry. These stains are often difficult to remove and can make your home look less clean and well-maintained.
- Health Concerns: While hard water isn’t harmful to drink, the scale buildup it causes can impact plumbing systems and potentially lead to bacterial growth. Stagnant water trapped by scale deposits can become a breeding ground for bacteria, posing a health risk.
How Water Softeners Combat Hard Water
Thankfully, water softeners can effectively address hard water issues. Here’s how they work:
Ion Exchange Process
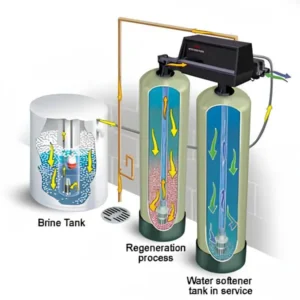
Water softeners use a process called ion exchange to remove calcium and magnesium ions from the water, replacing them with sodium ions. This exchange process takes place in a resin tank filled with small beads that carry a negative charge. The positively charged calcium and magnesium ions are attracted to the beads, which are coated with sodium ions. As the hard water passes through the resin tank, the calcium and magnesium ions are swapped with sodium ions, resulting in softened water.
This process is highly effective in reducing the hardness of water. The resin beads are periodically regenerated by flushing them with a salt solution, which replenishes the sodium ions and prepares the system for another cycle of softening.
Reverse osmosis is an alternative method of softening water that is optimal for homes in areas with extremely poor water quality. Read more about reverse osmosis here.
Benefits of Water Softeners
- Prevent Scale Buildup: By removing the minerals that cause scaling, water softeners help keep your pipes, appliances, and water heaters functioning efficiently. This not only extends the lifespan of your equipment but also reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs.
- Improve Soap Efficiency: Soft water allows soap to lather better and rinse away more easily, reducing soap scum and making cleaning easier. You’ll notice your laundry is cleaner, your dishes are spot-free, and your personal care products work more effectively.
- Softer Skin and Hair: Without the drying effects of hard water minerals, your skin and hair can feel softer and healthier. Soft water helps maintain the natural moisture balance of your skin and hair, reducing dryness and irritation.
- Stain-Free Fixtures: Soft water prevents the mineral deposits that cause stains on fixtures, dishes, and laundry. Your home will look cleaner, and you’ll spend less time scrubbing away stubborn mineral stains.
- Extended Appliance Lifespan: By preventing scale buildup, water softeners can help extend the life of your appliances and reduce maintenance costs. Appliances like dishwashers, washing machines, and water heaters will operate more efficiently and last longer with soft water.
Wrapping Up
Understanding what hard water is and the impact it can have on your home and daily life is crucial. By recognizing the signs of hard water and utilizing water softeners, you can mitigate its negative effects and enjoy a more efficient and comfortable living environment. If you’re dealing with hard water, investing in a water softener is the solution you need. Contact us today for help buying your system!
FAQs About Hard Water
Is hard water safe to drink?
Yes, hard water is safe to drink. It’s not harmful to your health but can cause issues with plumbing and appliances over time.
How can I test my water hardness?
You can use a home water test kit or send a sample to a laboratory for a detailed analysis.
What are some signs of hard water in my home?
Look for scale buildup on faucets and fixtures, soap scum in sinks and tubs, and mineral stains on dishes and laundry.
Share:
Talk to A Water Quality Expert
Shop Our Products

Freedom RV Water Softener System
Specifically for RV and fifth-wheel owners, this high-quality system guarantees your RV’s water is pure,



Why Water in the Bottom of Your Water Softener Isn’t Always a Bad Thing
Water in the bottom of your water softener’s brine tank can be normal, especially in wet brine systems where water is necessary for dissolving salt. Understanding the role of the brine tank and how it works can help you determine when water accumulation is typical and when it might indicate a problem.

Annual Water Softener Maintenance Checklist
Performing annual maintenance on your water softener prevents mineral buildup, ensures efficient operation, and extends its lifespan. Our checklist includes: a) checking salt levels, b) cleaning the brine tank, c) breaking up salt bridges, d) cleaning the resin tank, e) inspecting valves, and f) flushing the system. Regular maintenance keeps your water softener running smoothly and protects your investment.

Water Softener Grain Capacity Guide
Choosing the right water softener grain capacity is the most cost-effective way to soften your water. This guide explains what GPG (grains per gallon) means, how to calculate your required grain capacity, and what a resin bed is.
Join Our
Newsletter
Get the latest information, and exclusive offers on water softening and purity solutions
