Water Softener Grain Capacity Guide

Shop Our Products

Freedom RV Water Softener System
Specifically for RV and fifth-wheel owners, this high-quality system guarantees your RV’s water is pure,



What is Water Softener Grain Capacity?
Water softener grain capacity might seem complicated, but it is simpler than you might expect. To put it simply, grain capacity is how much hard water a water softener can remove before it needs maintenance.
Water contains minerals like calcium and magnesium that create what is known as hard water. Grain capacity measures how many of these mineral “grains” your water softener can remove before it needs to regenerate or clean itself. Soft water comes with a variety of benefits like reduced water staining and longer appliance life.
Grains Per Gallon (GPG)
Grains per gallon, or GPG, is how we measure water hardness. A grain is equal to 64.8 milligrams of calcium carbonate. It tells you exactly how many mineral grains are in each gallon of water. Here’s a breakdown of hardness levels
- 0–3 GPG: Soft Water
- 4–7 GPG: Moderate Hardness
- 8–10 GPG: Hard Water
- 11+ GPG: Very Hard Water
| Grains Per Gallon | Softness Level |
|---|---|
| 0-3 | Soft Water |
| 4-7 | Moderately Hard Water |
| 8-10 | Hard Water |
| 11+ | Very Hard Water |
Why the Right Grain Capacity Matters
Picking the right grain capacity helps your water softener work as efficiently as possible. The right grain capacity will provide a range of benefits, including less maintenance, more efficient softening, and a longer lifespan for your water softener.
How to Choose the Right Grain Capacity for Your Needs
Choosing the right water softener grain capacity starts with knowing your water’s hardness. GPG directly impacts the grain capacity you’ll need for your system. In basic terms, the harder your water, the more grain capacity your water softener will require.

Steps to Choosing the Right Grain Capacity for Your Home
Step 1: Test Your Water Hardness
Knowing your exact water hardness is the first step in selecting the right water softener. Test your water to determine how hard your area’s water is. This prevents you from buying a system that’s too large or too small.
Testing methods include DIY test kits, which are more affordable, or professional testing services. These services are more expensive, but you will have more accurate and in depth water quality data.
Visual Suggestion for Designer: Design an infographic showing the steps for using a DIY water hardness test kit. Include estimated costs, ease of use, and a comparison with professional testing.
Step 2: Calculate Your Daily Softening Need
Use this formula to determine required grain capacity: Daily Water Usage (gal) × Water Hardness (GPG) = Daily Grain Removal Need
In our calculations, we are assuming a daily water usage of 80 gallons per person, and a fairly hard water level of 10 GPG. Your own water hardness may vary, so it is important that you test your own water to make more accurate calculations.
Example calculations
- 1 person (80 gal x 1 person) = 80 gal
- 80 gal × 10 GPG = 800 grains/day
- 2 people (80 gallons x 2 people) = 160 gal
- 160 gal × 10 GPG = 1,600 grains/day
- 4 people: (80 gallons x 4 people/day) = 320 gal
- 320 gal x 10 GPG = 3,200 grains/day
Step 3: Calculate Weekly Grain Requirement
When choosing a water softener, match your daily grain removal to the system’s capacity.
| # of People | Daily Water Usage (day) | Daily Grain Need (Gal/day X 10 GPG) | Weekly Grain Need (Daily Grain X 7) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 gallons | 800 grains | 5,600 grains |
| 2 | 160 gallons | 1,600 grains | 11,200 grains |
| 4 | 320 gallons | 3,200 grains | 22,400 grains |
Once you have calculated your grain capacity requirements, round up to the nearest standard water softener capacity to determine the best fit for you. Standard capacities typically increase in increments of 8,000 or 16,000 grains.
Common Capacities (Grains)
- 16,000
- 24,000
- 32,000
- 40,000
- 48,000
- 64,000
- 80,000
Read more Tips on How to Choose the Right Water Softener

Why Choosing the Proper Grain Capacity Matters
The High Cost of Under-Sizing
Picking a water softener that’s too small for your home can cause several problems, increasing your long term costs.
- Frequent regeneration cycles wear down your system faster
- Reduced efficiency means your water won’t be as soft as it should be
- Higher salt consumption increases your operating costs
- Increased strain on the resin bed leads to more maintenance expenses
Does Over-Sizing Hurt?
Bigger isn’t always better when it comes to water softeners. Oversized systems tend to lead to many inefficiencies.
- Unnecessary upfront costs
- Waste water during regeneration
- Slow operation for smaller households
- Lead to more complex maintenance requirements
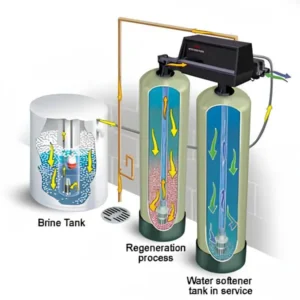
What is a Resin Bed?
What Resin Beds Do
Your water softener works in steps. First, hard water enters the tank and passes through a layer of tiny resin beads, known as the resin bed. The resin beads catch minerals, leaving the water softer as it comes out.
After a while, the beads fill up and stop collecting minerals. That’s when the system goes through regeneration, rinsing the beads with a salty brine solution to refresh them. This cycle keeps your resin bed ready to keep softening water.
Maintaining the Resin Bed
Just like any other part of your water softener system, the resin bed needs a little upkeep to stay at its best. Here are some basic tips to keep it working smoothly
Use the Right Salt
Always use high-purity salt specifically made for water softeners like evaporated salt pellets or solar salt. These dissolve more efficiently, produce fewer impurities, and help prevent buildup that can clog the resin bed over time.
Clean the Resin Bed Periodically
Over time, iron, sediment, and other contaminants can accumulate on the resin beads. Using a resin bed cleaner or following the manufacturer’s instructions can remove these deposits. Routine cleaning boosts performance and extends the life of your resin bed.
Watch for Warning Signs
If you notice your water feeling hard again very quickly, or if the softener is regenerating more often than normal, the resin bed could be functioning improperly. It is important to address these problems as soon as you can. Whether by cleaning, adjusting settings, or adding a resin cleaner, you will be preventing future problems.
Common Misconceptions About Grain Capacity
1. “Bigger Is Always Better”
- Myth: The larger the grain capacity, the better the performance.
- Reality: An oversized softener usually means you’re using more salt, water, and money than you actually need. It makes more sense to choose a capacity that fits your home’s water use so you don’t waste resources.
2. “Grain Capacity Equals Water Quality”
- Clarification: Grain capacity measures how well the system removes hardness minerals, but that doesn’t mean it’s purifying your water. It won’t remove contaminants like chemicals or bacteria. If you’re worried about overall water quality, consider additional filtration methods.
3. “Regeneration Frequency Doesn’t Matter”
- Clarification: Frequent regenerations mean you’re using more salt and putting extra strain on the resin bed. This leads to more wear and tear and higher costs. Ideally, your grain capacity should match your usage, reducing how often you need to regenerate.
Still Unsure About Grain Capacity?
Testing your water hardness, adding up your daily water usage, and calculating your proper grain capacity can be confusing. Consulting with a water quality expert can make choosing the right softener a quick, easy process.
Find Your Water Softening Solution Today | Contact Patriot Water System
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Difference Between PPM and GPG in Water Softeners?
GPG, or grains per gallon, is the standard unit used primarily in the United States to measure water hardness. One grain per gallon is equivalent to approximately 17.1 parts per million. PPM, or parts per million, is a more universal, metric-based measurement of water hardness. Many water tests report hardness in PPM, which can be converted to GPG by dividing the PPM value by 17.1. Here is a quick conversion: 1 GPG = 17.1 PPM
What Happens If I Set My Water Softener Hardness Too High?
If the hardness setting on your water softener is higher than your actual water hardness the softener will regenerate more frequently than it should. This ends up wasting more salt and increasing your maintenance costs. Your water softener will also regenerate more often, which means leads to accelerated wear on the system’s components.
What Number Should a Water Softener Be Set At?
On most water softeners, the number setting should match your actual water hardness measured in grains per gallon. As an example, you should set your water softener to the number “10” if the water in your region has water hardness of 10 grains per gallon. If your water has high levels of iron, you may need to adjust the setting on your softener even higher by 3-5 GPG.
How Many Grains Should I Get on My Softener?
To determine the grain capacity you need your water softener to have, use this formula: Daily Water Use × Hardness × Days Between Regeneration = Required Capacity
Example for a household of four people each using about 80 gallons per day, and water with a hardness of 10 GPG, aiming for a 7-day cycle:
(4 people × 80 gal/day) × 10 GPG × 7 days = 22,400 grains
Rounding up to the next standard size (24,000 grains) ensures you have a margin for variations in usage or hardness.
Share:
Talk to A Water Quality Expert
Shop Our Products

Freedom RV Water Softener System
Specifically for RV and fifth-wheel owners, this high-quality system guarantees your RV’s water is pure,




Top 5 Water Softeners For Well Water
The best water softener for well water is a salt-based system like the Patriot 2, as it effectively removes minerals like calcium and magnesium that cause hard water. This guide reviews the top 5 water softeners to keep your well water clean and safe.

Annual Water Softener Maintenance Checklist
Performing annual maintenance on your water softener prevents mineral buildup, ensures efficient operation, and extends its lifespan. Our checklist includes: a) checking salt levels, b) cleaning the brine tank, c) breaking up salt bridges, d) cleaning the resin tank, e) inspecting valves, and f) flushing the system. Regular maintenance keeps your water softener running smoothly and protects your investment.
Why Water in the Bottom of Your Water Softener Isn’t Always a Bad Thing
Water in the bottom of your water softener’s brine tank can be normal, especially in wet brine systems where water is necessary for dissolving salt. Understanding the role of the brine tank and how it works can help you determine when water accumulation is typical and when it might indicate a problem.
Join Our
Newsletter
Get the latest information, and exclusive offers on water softening and purity solutions
